Pharmaceutical water must meet quality standards - it participates in the entire production process of pharmaceuticals, including formulation, cleaning, and disinfection. Therefore, pharmaceutical water is an important component of the pharmaceutical production process, and it is necessary to ensure that the pollution risk of pharmaceutical water in the design of preparation, storage, and distribution systems is controlled, and to maintain that the pharmaceutical water system can provide pharmaceutical water and steam that meet quality requirements.
Composition of pharmaceutical water system
The pharmaceutical water system mainly consists of a preparation unit and a reserve and distribution system, while the pharmaceutical steam system mainly consists of a preparation unit and a distribution system, which are similar systems. Among them, the preparation unit mainly includes a softening water machine, a purified water machine, a high-purity water machine, a distilled water machine, and a pure steam generator. Its main function is to continuously and stably treat the raw water to meet the requirements of the pharmacopoeia or internal control standards of the enterprise. The reserve and distribution system mainly includes reserve units, distribution units, and water point network units.
Classification of pharmaceutical water
From a standard perspective, pharmaceutical water can be classified into pharmacopoeia compliant pharmacopoeia water and non pharmacopoeia water. Among them, non pharmacopoeia water refers to pharmaceutical water that is not included in the pharmacopoeia but can be used for production, such as drinking water, softened water, distilled water, reverse osmosis water, ultrafiltration water, deionized water, laboratory water, etc. Non pharmacopoeia water needs to meet at least the requirements for drinking water. If necessary, non pharmacopoeia water can also be used in pharmaceutical production operations, such as cleaning production equipment, as raw materials for raw material production, and laboratory applications. However, the pharmacopoeia stipulates that the preparation of formulations must use injection water, so whether it is pharmacopoeia water or non pharmacopoeia water, it must meet the prescribed microbial limit standards.
From the perspective of usage, pharmaceutical water is mainly divided into two categories: bulk water and packaging water. Bulk water, also known as raw material water, refers to the water used in pharmaceutical production processes, while packaging water, also known as finished water, refers to the packaged finished water produced according to pharmaceutical processes. The bulk water recognized by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia includes purified water and injection water, while the approved packaging water includes sterilized injection water. The bulk water recognized by the European Pharmacopoeia includes purified bulk water, high-purity water, and injection water, while the approved packaged water includes purified bulk water and sterile injection water. The bulk water recognized by the US Pharmacopoeia includes purified water, hemodialysis water, and injection water, while the approved packaging water includes antibacterial injection water, sterile inhalation water, sterile injection water, sterile rinse water, and sterile purified water.
Water production process management
The commonly used process water includes: raw water, which refers to the water before entering the water treatment process; Purified water is pharmaceutical water produced from tap water after being filtered through multiple media, activated carbon, softener, security filter, reverse osmosis, and EDI processing; Injection water is made from purified water by high-temperature heating and distillation, hence also known as distilled water; Pure steam is steam produced by heating purified water at high temperatures.
Preparation work before water production
Before starting up the equipment, all systems should be checked first. The main inspection items for the preparation and storage systems of purified water, injection water, and pure steam generators are similar: check the power supply voltage, tap water supply (purified water storage tank water level), industrial steam pressure, compressed air pressure, check the connections and pipelines, and ensure that there is no leakage or leakage in the storage channel; Check the status of the respirator valve in the water storage tank, test run the equipment, and check the working status of all components.
In addition, each system also has some separate inspection items: the purified water system should also check the liquid level of the dosing tank and the status of each manual valve; The injection water system should first check the status of the respirator valve in the injection water storage tank, check whether the respirator temperature reaches 85 ℃, and then try to run the equipment again to check the working status of all components; Both injection water and pure steam generator systems should inspect the valves of industrial steam pipelines and discharge condensate from the pipelines.
Water production operation method
The preparation and storage process of purified water includes: heating of the raw water tank, water production, and circulation; Check the salt water tank, add industrial salt, prepare saturated salt water, and fill in the dosing record form; Check the alkali water tank, add sodium hydroxide solution, and fill out the solution preparation record form. The preparation and storage process of injection water can be summarized as preheating, water preparation, circulation, and insulation. The process of preparing clean steam is similar, mainly including preheating, gas production, and sampling.
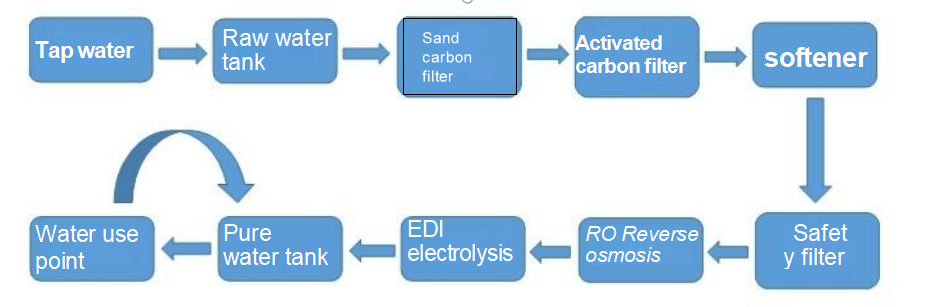
Process flow chart of purified water preparation and distribution system
Water system monitoring and management
The monitoring and management of water systems should start with water quality monitoring. Only when the water has passed QC inspection and proven to be of qualified quality, can the engineering personnel notify the production personnel to use it. Engineering personnel should observe the online conductivity at all times to ensure that the conductivity is ≤ 1.0 μ Only allow water to enter the storage tank at S/cm; If the conductivity of the circulating water in the storage tank slowly increases to close to 1.0 when the continuous water consumption is not high μ S/cm, at this point, some pure water needs to be discharged and treated to maintain the conductivity of the circulating water in the storage tank at ≤ 1.0 continuously μ Within the range of S/cm. Additionally, attention should be paid to the difference between warning limits and action limits. The alert limit is usually determined by trend analysis based on the normal operation level and detection data of the system. If it only exceeds this limit, there is no need to further process the system. Increasing the corresponding monitoring items or monitoring frequency is sufficient. But when the system reaches the action limit, in order to prevent the system from being unqualified and causing losses, it is necessary to investigate and handle the system.
Secondly, daily monitoring plans for each system should be developed. The raw water used for company water production should be sampled and fully tested every three months, including characteristics, pH, and microbial limits. For the purified water system, it should be ensured that the total water supply outlet, total return outlet, and purified water storage tank of the purified water system are sampled and fully inspected every week. Other support points should complete one round of testing every month, and the designated personnel should develop a sampling plan for the current month. For the purified water point in the injection workshop, if it is not used for more than a month, it may not be monitored. At this time, the production department or QC (quality control) can submit a planned deviation and apply for the suspension of the use of the purified water point. QA (quality assurance) will hang a sign at the water point saying "Not applicable for the production of GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) related products". If there are no special circumstances, the water point should be monitored three times before use to ensure that the physical and chemical indicators are qualified and the microbial limit results are qualified before the production of the product can be released. Purified water points that have been out of use for less than a month can be put into use after normal monitoring. In addition to monthly monitoring, attention should also be paid to daily monitoring and testing of the purified water system, including characteristics, pH, nitrate, nitrite, ammonia, conductivity, total organic carbon, non-volatile substances, heavy metals, and microbial limits.
For the injection water system, the total supply outlet, total return outlet, and total production outlet should be sampled and tested once a day for conductivity, total organic carbon (TOC), microbial limits, and bacterial endotoxins. Other water use points should ensure sampling on a weekly basis, taking turns every day, and completing one round of testing per week. If the injection water system is shut down for more than a week, the injection water system should be cleaned and disinfected again. The total water point and usage point of the injection water should be monitored three times (with the same testing items as above). After ensuring that the conductivity, TOC, and bacterial endotoxins are qualified, the workshop can use them to produce GMP batch products. Only after the microbial limit results are qualified can the production products be released. If the production cycle is less than one week, it should be ensured that all usage points are monitored within that cycle.
For pure steam systems, samples should be taken once a week from the main point and once a month from the support point. If not in use, no samples should be taken. The testing items for daily monitoring of pure steam systems are similar to those of purified water systems, except that bacterial endotoxins need to be tested.
Disinfection and sterilization management
Pasteurization is a commonly used disinfection method. At a certain temperature, the lower the temperature, the slower the bacterial reproduction; The higher the temperature, the faster the bacteria reproduce; But if the temperature is too high, bacteria will die, and different bacteria have different suitable growth temperatures as well as heat and cold resistance. Pasteurization is actually the use of the heat-resistant characteristics of pathogens, using appropriate temperature and insulation treatment to completely kill them. The activated carbon filters used in the preparation system are generally pasteurized (disinfected with hot water at 80 ℃ to 85 ℃), while the storage and distribution system is generally disinfected using ultraviolet radiation. The following text will take the operation of the equipment used by Renfukang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. as an example to explain in detail the sterilization management of the system.
For the injection water preparation system, if the injection water machine is not frequently turned on and stopped for a long time, the water storage tank needs to be emptied first. Before preparing injection water again, the parameter setting interface usually automatically sets the self sterilization temperature to 121 ℃, the inlet water flow rate of the self sterilization equipment to 0.3 t/h, and the self sterilization time to 30 minutes. At this time, "multi effect automatic" is activated, and the equipment will start self sterilization first.
When disinfecting the distribution system, the injection water should first reach a liquid level of 0.8-1 m, then click on "Distribution Process" to manually operate, click on "Transfer Pump" to start the cycle, and then click on "Heat Exchanger" to select disinfection. Generally, the disinfection mode is set as follows: disinfection temperature of 121 ℃, disinfection time of 30 minutes. Afterwards, the system will automatically run disinfection mode.
Red rust removal management
In the pharmaceutical industry, red rust is generally a direct product of metal corrosion, which can cause damage to system components, pipeline leakage, filter clogging, and may also cause heavy metal pollution to the water quality of pharmaceutical water. So it is necessary to regularly clean and disinfect the purified water system and injection water system, and keep records to remove microorganisms attached to the surface of the system and prevent the formation of red rust. Once red rust appears, pharmaceutical companies need to pay more attention. If red rust appears on the tank body, they should immediately seek relevant parties for passivation treatment; If red rust appears on the pipeline, it should be replaced in a timely manner.
Maintenance and management of water production system
For the purified water system, the incoming water tank should be cleaned once a year, the raw water tank should be disinfected and drained every two months, the purified water tank and distribution system should be pasteurized once, and the surface of the raw water tank should be cleaned once a month.
For the injection water system, it is necessary to regularly check the surface dust of the injection water tank, instruments and clean the frequency converter, and clean them in a timely manner; Check all pneumatic valves and electrical cabinet ventilation fans, and promptly remove dust inside the electrical cabinet; Check and verify sensors (such as temperature sensors, pressure gauges, pressure sensors, conductivity and flow meters, etc.), check and verify safety valves, inspect/replace respirators, check the noise, bearings, and water seals of purified water pumps and injection water circulation pumps; Check the fouling situation of the heat exchanger and arrange for cleaning.
For pure steam systems, safety valves, heat exchangers, pure water pumps, instruments and sensors, heat exchangers, power switches and signal indicators, DC power supplies, various electrical components (such as AC contactors and relays), programmable controllers (PLC), recorders, human-machine interface HMI, various pneumatic valve components, power supply wires in control cabinets, drain valves, and equipment scale should be checked/cleaned regularly; Timely inspect/replace the mechanical seals and motor bearings of the water pump; Check if there is any running or dripping in the pipeline; Check if the equipment is grounded/insulated.
Water production equipment physical picture
Other precautions
Operators must strictly follow the job standards for operation and must pass the job training before entering the job for operation. The operating part of the equipment must have protective covers or warning signs, and it is prohibited to stack items near the operating equipment; When operating steam valves, preparing saturated salt water and sodium hydroxide solutions, operators should wear protective equipment such as gloves and goggles.
After disinfecting the pipeline, the water tank needs to be emptied and water needs to be remade; The preparation system and distribution system need to close the respirators on the storage tank during disinfection; Before making water (after disinfection is completed), the respirator must be fully opened to avoid high temperature burns; Since both purified water and injection water in the water production room require constant circulation, when not in production, the purified water should be switched from "automatic water production" to "manual water production" in the automatic mode of the human-machine interface; On the other hand, the injection water needs to be switched from "multi effect automatic" to "multi effect manual", and the "heating" mode of the multi effect distribution system heat exchanger needs to be activated. The pure steam system can switch from "automatic" to "manual" and then turn off the power when the temperature drops to room temperature. During the production process, engineering personnel should follow the cleaning standard operating procedures and fill out equipment operation records.
Conclusion
Due to the direct impact of pharmaceutical water on the quality of drugs, the pharmaceutical water system can continuously provide stable and qualified pharmaceutical water, which is a prerequisite for ensuring the quality of drugs. By adopting reasonable operations and daily monitoring measures, and doing a good job in the maintenance and management of pharmaceutical water systems, we can fundamentally prevent contamination of pharmaceutical water and ensure the quality of drugs.
Jinzong Enterprise has over 20 years of experience in designing and manufacturing pharmaceutical equipment, and can provide one-stop turnkey engineering services. Welcome to inquire or visit the factory for guidance!




